Gold mining underground mining and open-pit mining division. For the vein gold deposit, underground mining or open pit mining can be used; for sand gold deposits, open pit mining is generally used.
     1. Mine shaft and its classification
     In order to extract the buried deep vein gold deposit, a series of wells must be excavated from the surface to the ground to connect the ore body with the ground, thus forming a complete transportation, lifting, pedestrian, ventilation, drainage, power supply, air supply, Systems such as water supply and filling, which are collectively referred to as mine shafts (see Figure 1). Mine shafts can be divided into two main categories:
figure 1 
     (1) Drainage room: refers to the roadway with little difference in length and width. Usually named according to their use, such as underground lifting machine room, mining warehouse, pump house, substation, machine repair room, explosives warehouse, motor garage, dispatching room, etc.
     (2) Roadway: refers to the well lane with a length much larger than the width. According to the angle between the long axis direction and the horizontal plane, it can be divided into: 1) Vertical roadway: the long axis direction is perpendicular to the horizontal plane. Such roadways mainly include shafts, blind shafts, vertical shafts, vertical patios, and the like. The shaft has access to the surface, which is mainly used to raise ore, waste rock, materials, equipment, personnel and ventilation. It is generally referred to as the main well for upgrading ore and the auxiliary well for other tasks. Blind shafts do not have direct access to the surface and have the same function as the shaft. Vertical chutes use gravity to dig ore or waste rock. The vertical patio is used for personnel access, ventilation, transportation of materials and equipment and for prospecting. 2) Inclined roadway: The direction of the long axis is at an oblique angle to the horizontal. Such roadways mainly include inclined shafts, blind inclined shafts, inclined shafts, inclined patios, etc., and the uses are the same as shafts, blind shafts, vertical shafts, and vertical patios. 3) Horizontal roadway: The direction of the long axis is horizontal, but it has a very steep slope (2%~5%) for transportation and drainage. This kind of roadway mainly includes Pingyi, Shimen, vein inner roadway, pulse outer roadway, and cross roadway (through the vein roadway), etc., which are used for personnel transportation, transportation, ventilation, drainage, prospecting and so on. Pingyi has a direct export to the surface, a main flat for transporting ore, and a subordinate flat for other tasks. Shimen has no exit and leads directly to the surface. The alleys are parallel to the ore body, and there is no direct outlet to the surface. The excavation in the ore body is called the in-pulse flat roadway, and the excavation in the surrounding rock is called the outer roadway. The cross lane is perpendicular to the ore body and is excavated in the ore body. [next]
     2. Division of mining units of vein gold deposits
     The vein gold deposit is generally divided into ore fields, and the ore fields are divided into mine fields. The well fields are divided into stages, and the stages are divided into ore blocks. The nugget is the most basic mining unit.
Ore field: A deposit or part of a mine. The size of the ore field is determined by the natural conditions of the deposit. An independent production unit generally marked by a main well or main flat is called a mine field (pit).
     Minefield: An ore body or part of a mine that has been mined at the pit. In production practice, a large ore body or several ore bodies adjacent to each other are often classified as one well field for independent mining.
     Stage: In the direction of the ore body along the inclined direction of the ore body, at a certain vertical distance, the top-down roadway (main transportation lane) is merged from the top to the bottom, and the ore body is divided into one ore section in the vertical direction. The segment is called the phase, also known as the middle segment. The height of the stage is the vertical distance between the transport lanes of the two adjacent stages. The scope of the stage: the direction of the mine is limited to the boundary of the well, and is limited to the two main transport lanes above and below the slope (see Figure 12).
figure 2 
     Nugget: In the stage roadway, the patio is drilled at a certain distance along the ore body, and the stage is divided into several blocks, each of which is called a nugget (mining area), as shown in Fig. 2.
     3. Gold mining underground mining sequence
     The mining sequence of adjacent ore bodies: firstly mining the ore body located on the upper plate, and then mining the ore body of the lower plate.
     Mining sequence of minefield: When the deposit is divided into several wells, it is generally preferred to open wells with high grade, good selectivity, small amount of infrastructure construction, and transportation, water supply and power supply.
     The mining sequence of the stage: there are two types of uplink and downlink. Downward mining is carried out from top to bottom, one by one (or several) stages, while the upside is reversed. Downstream type is used in production practice because of low investment, fast production, easy exploration and good safety.
     Mining sequence of ore blocks: According to the position of the mining work relative to the main development roadway (main well, main level), it is divided into three types of mining: 1) Forward type: After the stage is leveled, the distance from the main well From the nugget, it will be harvested sequentially to the boundary of the minefield; 2) Retreat: After the tunnel is drilled to the boundary of the minefield, it starts from the nugget at the boundary of the minefield and is sequentially recovered in the direction of the main well, which has more applications in production; 3) Hybrid: Start with the forward type, and use the backward type after the stage is cleared. [next]
     4. Deposit mining steps
     The underground mining of the vein gold deposit must go through three major steps: development, acquisition, cutting and recovery. Mineral deposit development is the basic preparation for mining, but it is not sufficient preparation work. On the basis of completion of development, it is necessary to carry out the mining and cutting. The recovery work can only be carried out after the acquisition and cutting are completed. In the initial stage of mining, the above three steps are carried out in sequence; in the production period, they are also carried out sequentially in the same section, but may be carried out simultaneously in different sections.
     (1) Pioneering: underground mining of vein gold deposits must firstly excavate a series of wells from the surface of the ore body to form a complete transportation, lifting, pedestrian, ventilation, drainage, power supply and air supply between the deposit and the surface. , water supply and filling systems. The construction of the project is called development.
     (2) Alignment and cutting: On the basis of completing the pioneering project, a series of roadways will be excavated, and the stage will be divided into ore blocks, and the mining conditions for pedestrians, ventilation, transportation, rock drilling and ore mining will be created in the ore blocks. Prepare for work, call it. The roadway that the excavation is excavated is called the mining lane. The layout and type of mining lanes vary with mining methods. Common mining lanes have stage transportation lanes, vein roadways, ventilation, pedestrians, transporting patios, rock drilling and alleys, rock drilling patios, cutting patios, bottoming roadways, electric roadways, loading roadways, ore draining wells, etc. .
     The cutting is in the ore block that completes the mining project, and opens up a free space for the returning ore to open a free space.
     (3) Mining: directly obtaining ore from the completed and cut ore. It has three production processes: mining and mining (also known as collapse mining), transportation and ground pressure management.
     At present, the widely used method of falling mine is rock drilling and blasting method, that is, drilling a hole in the ore body, filling explosives and detonating materials, and breaking the ore by explosive explosion and separating it from the ore body.
     Transportation is the transfer of ore from the location of the break to the loading of the stage transport lane.
     Ground pressure management, also known as mining (area) field support, is to take various technical measures to ensure the safety of the goaf during the mining process, and there are two indirect and direct methods. The indirect method is to try to maintain the stability of the roof and the two surrounding rocks in the goaf; the direct method is to directly support the exposed ore, the method is to reserve the pillar support (natural support), fill with waste rock, etc. Filling support (artificial support), supporting with pillars such as wood and leaving part of the ore to support the support.
     5. Deposit underground development method
     The underground development method of the vein gold deposit has two major categories: the single development method and the joint development method.
     The single development method is to use a kind of main development roadway to develop mineral deposits. Common single development methods are:
     (1) Pingyi Development Method (Fig. 3): The development method of exploiting the entire deposit by using Pingyi as the main development roadway. Zhaoyuan gold, Xiaoqinling Gold, Suichang gold, gold Yongsan, Yindongpo gold and gold and other luanchuan using this method.
image 3 
     (2) Shaft development method (Fig. 4): The development method of exploiting the entire deposit by using the shaft as the main development lane. This method is adopted in Jiaojia Gold Mine, Wulong Gold Mine, Honghuagou Gold Mine and Rushan Gold Mine. [next]
Figure 4 
     (3) Inclined well development method (Fig. 5): The method of exploiting the entire deposit by using the inclined shaft as the main development roadway. This method is adopted in Xincheng Gold Mine, Xiangxi Gold Mine, Honghuagou Gold Mine, Dongfeng Gold Mine, Yu'erya Gold Mine, Hedong Gold Mine and Gupao Gold Mine.
Figure 5  [next]
[next]
     The joint development method is a pioneering method that combines the above-mentioned several single development methods, such as the joint development method of Pingshuo and blind shaft (Fig. 7), the joint development method of shaft and blind shaft (Fig. 8), inclined well and blind inclined well Joint development method (Figure 9), joint development method with ramps, etc. Due to the limitations of the topography and the burial conditions of the deposit, the joint development method is adopted when only one of the above-mentioned development methods is unlikely or unreasonable.
Figure 7 Figure 8 

Figure 9 
     6. Overview of mining methods
     The underground mining method is a general term for the mining, cutting and mining operations carried out by mining ore from underground ore. There are many mining methods, which can be divided into four categories based on ground pressure management:
     (1) Empty field mining method: It is characterized by the stability of the pillar and the surrounding rock itself to maintain the goaf formed during the mining process, and the ore and surrounding rock are required to be stable. Such methods include comprehensive mining methods, room and pillar mining methods, subsection mining methods, and stage mining methods.
     (2) Mining and mining method: It is characterized in that the mining process temporarily retains part of the ore collected in the goaf to form a retained ore pile, and the retained ore pile acts as a falling ore working platform, and assists with the pillar to support and maintain the gob. The ore is required to be stable and the surrounding rock is moderately stable.
     (3) Filling mining method: It is characterized by the use of filling materials or other supports to maintain the goaf, which is suitable for ore bodies where the surrounding rock is unstable, the ore is valuable and the surface needs to be protected. Such mining methods include dry filling mining, hydraulic filling mining and cement filling mining.
     (4) Caving mining method: It is characterized that with the advancement of the mining face, the surrounding rock is plannedly collapsed, and the surrounding rock that collapses and swells fills the surrounding rock caving space of the goaf to control and manage the ground pressure. purpose. Such mining methods include wall caving method, stratified caving method, sub-column sublevel caving method, sub-column sublevel caving method and stage caving method. [next]
     Statistics from 1987 show that among the mining methods used in China's rock gold mines, the mining and mining method accounts for 42%, the filling and mining method accounts for 31%, the open field mining method accounts for 25%, and other methods account for 2%. At present, the underground mining of gold is paying more and more attention to the recovery of ore. The use of the filling and mining method has been increasing year by year, and the proportion of the mining and mining method has decreased. The following is a description of the more mining and mining methods used in rock gold mines, the dry filling mining method in the filling mining method, the hydraulic filling mining method and the cement filling mining method, and the comprehensive mining method in the open field mining method.
7. Mining and mining law
     The mining and mining method is that workers work under the exposed surface of the ore body and layer back to the ore from bottom to top. Each time a small part of the ore that collapsed (about one-third) is released from the bottom of the ore by its own weight, and the rest is temporarily retained in the goaf to form a workbench for re-mining, while supporting the surrounding rock. The role. The remaining ore is released after all the ore in the stope is taken. The schematic diagram of the mining and mining method is shown in Figure 10.
Figure 10 
     The mining and mining method is applicable to steeply inclined thin ore bodies with an inclination of more than 55°. The surrounding rock and ore of the ore body are stable, and the ore is not agglomerated and natural.
     8. Dry filling mining method
     The so-called dry filling mining method refers to a filling mining method using waste rock as a filling material. According to different sources of filling, it is divided into ordinary dry filling mining method and wall filling mining method. The difference between the two is that the filling of the former comes from the stope, which is usually called dry filling mining method; the filling of the latter comes from the surrounding rock of the ore body in the stope, which is also called mining and filling mining. The law or the selection of the mining method.
     (1) Ordinary dry filling mining method: Filling mining method that is layered back from the bottom up. As shown in Fig. 11, it is characterized in that the ore block is divided into a mine house and a mine column, and the mining column is first mined, and the mining house is harvested from the bottom to the top. With the upward movement of the mining face, the waste rock is filled with the waste rock layer by layer to maintain the surrounding rock of the upper and lower plates, and the working conditions for continuous mining are formed. After filling a layer, a layer of 8~10 cm thick concrete floor is laid on the upper part to reduce the depletion and loss of ore during mining and improve the efficiency of mining. The collected ore falls on the filling body and is then mechanically transported to a sloping mine that is placed in the filling body. This method is suitable for the mining of ore stabilized and the surrounding rock is unstable. [next]
Figure 11 
     (2) Cutting wall filling mining method: When mining a very thin vein with a thickness of less than 0.8 m, in order to ensure the minimum working width of the mining space, a certain width of surrounding rock has to be taken. The method of cutting the wall filling mining method is to separate (take down) the ore and surrounding rock according to the width of the mining width. The fallen ore is transported out of the ore chute, and the collapsed surrounding rock is filled as filling material in the goaf and used as the working platform for mining. . This method is suitable for mining two gangs of high-grade and extremely thin veins that are not mineralized, with obvious contact between veins and surrounding rocks.
     9. Hydraulic filling mining method
     The so-called water filling method refers to a method of mining slag, river sand, gravel and other fill goaf plants discharge beneficiation tailings or smelter force in the pipeline with water.
     The hydraulic filling mining method divides the ore into a mine room and a pillar, and first mines the mine pillar. The mine (or pillar) is divided horizontally or obliquely at a vertical height, and the recovery is carried out layer by layer from top to bottom. Each time a layer is collected, it is filled immediately, and a mine-boring well and a pedestrian patio (also used as a drainage well) are constructed along the filling body. After filling, the water in the filling material penetrates and flows out of the mining field through the filtering well, and the filling material is deposited to form a filling body. The upper part of each layer of filling body is covered with a strong cemented floor to reduce the depletion and loss of ore during ore mining and improve the efficiency of mining. The backing body supports the surrounding rock and serves as a workbench for continued mining. The collected ore falls on the filling body and is then mechanically transported to a sloping mine that is placed in the filling body. This method is suitable for mining ore bodies where the ore is stable and the surrounding rock is unstable.
     10. Cement filling mining method
     The so-called cement filling mining method refers to a mining method for filling a goaf with cement or its substitute and cemented filling made of de-sluice tailings or sand. There are two kinds of cemented filling materials: concrete and mortar, which are mainly transported by roadway and pipeline. It is developed on the basis of the hydraulic filling mining method. The purpose is to condense the filling into a whole with a certain strength to improve the mining conditions of the pillar, further reduce the loss and depletion of the ore, control the movement of the surrounding rock and protect the surface. . According to the driving direction of the mining face, the cement filling mining method can be divided into:
     (1) Upward stratified cement filling mining method: dividing the nugget into a mine house and a pillar; first mining the house, filling with cementing filler during the mining process, making the filling body an artificial pillar with sufficient strength; Force or dry fill back to the mining column. [next]
     (2) Down-layer stratified cement filling mining method: a top-down stratified mining, stratified filling, a mining method under the artificial cemented backfill. As shown in Figure 12, the mining level is stratified or inclined (10°~115°), leaving no top and bottom columns, ore ore and filling, pedestrian patio in the center of the ore block. The ore is collected and transferred to the lower stage transportation lane. The filling material is transported from the upper stage to the stope through the chute. With stratified recovery, a filling, pedestrian patio is constructed in the filling body. In the stratified mining, the cutting roadway is first connected to the chute and the filling, the pedestrian patio, and then returned to the ore. This method is applicable to ore bodies where mining ore and surrounding rock are not stable.
Figure 12 
     11. Comprehensive Mining Law
     The comprehensive mining method can divide the stage into ore nuggets. The mining work is carried out along the direction of the ore body or along the slope and the reverse slope. The whole layer is recovered and the ore collected is transported in the stope. During the process of propelling the working face, according to the stability of the rock in the top of the stope, the ore or lean ore in the ore body is left as a pillar with irregular shape, size and spacing to support the surrounding rock of the roof of the goaf. As shown in Figure 13. When mining smaller thickness ore bodies, it is also possible to support the roof surrounding rock with artificial pillars such as concrete rafts, rafts, waste gangues, and wooden pillars.

     The comprehensive mining method is applicable to ore bodies where the ore and surrounding rock are stable, the inclination angle is horizontal, gently inclined, inclined, and the thickness is less than 5 meters.
Heat Treated Steel Bar And Tube
HEAT TREATED STEEL BAR AND TUBE
Heat treated steel bar is produced by heating and cooling in different temperature based on the steel grades to improve the steel bar mechanical properties or machinability for various industrial applications. Heat treated steel bar includes annealed steel bars, Normalized Steel Bar, quenched and temper qt steel bar.
Annealed Steel Bar has better ductility and lower hardness, which can be easier to be machined. The annealing processing is usually widely used for steel grade with higher carbon content above 0.5%. However, some low carbon steel also requires to do annealing for special usage such as 20CrMnTi gear steel. For some special material such as 20CrMnTi gear steel and GCr15 such bearing steel, spheroidizing annealing is often required.
Normalized steel bar sometime is also one kind of annealing processing. It mainly changes the grain to remove the impurities in steel and improves the strength and hardness. For some hot rolled steel bars, to keep the basic mechanical properties, normalizing is often used.
Quenching and Tempering, abbreviated as Q&T is a king of processing that strengthen or harden steel bars by heating the materials and then cooling in water, oil or other liquid medium, that rapidly the change from austenite to perlite to get the proper properties for various usage. The quenched & tempered steel bar materials are usually with carbon from 0.30% - 0.60%, it is widely used as merchant bars in components of various machines.
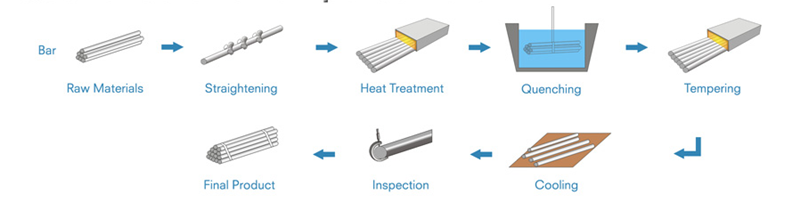
Our advantages on producing heat treated steel bars:
1) Big stocks of hot rolled round bars or wire rods as raw materials
2) Wide range of Cold Drawn Steel Bar sizes: from 10mm to 150mm
3) Different cold drawing medias powder or oil to get different surface
4) Straightening machines to get better straightness up to 0.5mm/m
5) Grinding and polishing machines to get better roughness upto 0.4um
6) Heat treating furnaces to adjust the mechanical properties
7) Full sets of testing equipment to test the sizes, mechanical properties and microstructure.
8) Multiple packages to avoid broken packages and anti-rusty
4140 steel tube,Round Steel Tubing,Heat Treated Steel Tube,Heat Treated Steel Bar And Tube,S355JR steel tube
SHANDONG LE REN SPECIAL STEEL CO., LTD. , https://www.sdhighstrengthsteelbolts.com