How to make full use of the functions of the existing EMS in the electricity market environment is an important issue. From the electricity market point of view, the EMS can obtain a large amount of real-time and processed grid operation data, which are necessary for the settlement system [1], the information release system [2] and the transaction management system [3]. Therefore, EMS can be seen as an important part of the electricity market operating system.
1 Relationship between PMOS and EMS Figure 1 shows the data flow diagram for each subsystem of EMS and PMOS.
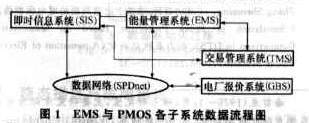
In order to carry out power market operation and assessment, it is necessary to obtain operational data with time scales from the EMS, such as grid frequency curve, actual load curve, actual output curve of the unit, reserve capacity curve, control commands and adjustment records, and voltage detection point voltage curve. , Unit start and stop record and switch action record. In addition, the EMS needs to provide minute-level real-time data to the SIS, such as system frequency, total output, total load, power plant and substation operating conditions (unit output, line flow, bus voltage, switch status, etc. ).
The EMS software functions of the 2EMS are mainly classified into three levels: data acquisition level (SCADA), power generation plan level, and network analysis level. The implementation of the electricity market has various degrees of impact on EMS software functions at all levels.
2.1 Data Acquisition Level Data Acquisition and Monitoring (SCADA) is the overall interface between EMS and telecontrol. The EMS obtains real-time data and sends control signals back to the system. SCADA provides real-time data to the energy management level and network analysis level of the EMS; the energy management level sends control signals to the power system through it; the network analysis level sends back measurement quality information to it.
In the power market, various power grid operations required for the preparation of electricity purchase plan, safety check before the power generation plan is issued, and automatic power generation control (AGC), reactive service, and mandatory backup auxiliary service plan are required. The telemetry and remote-sensing data needs to be realized through the SCADA acquisition of the generator's active, reactive, and port voltages. Therefore, under the power market environment, various grid data collected by SCADA in EMS can be used as the data source for power market application. PMOS does not need to build a separate data acquisition system. PMOS compiles plans to send and purchase electricity, especially to real-time dispatching commands with remote-control and remote-adjusting units, which still need to be implemented through the SCADA system.
2.2 Power Generation Plan Level 2.2.1 Automatic Generation Control In the traditional EMS, Automatic Generation Control (AGC) is one of the most important control functions, which can improve the grid frequency quality, economic efficiency and management level. The main functions of AGC include: Calculation of regional control deviation (ACE), calculation of AGC unit base point power and power adjustment, AGC mode, power plant control (PLC), unit control mode and adjustment mode, etc., to realize regional fixed frequency control and constant exchange Power control and tie line deviation control ensure that the regional frequency and the exchange power of the inter-regional tie line are at a certain level.
In the electricity market, AGC is one of the functions of the auxiliary service. Its role is still to maintain the balance between the power generation and the load power and ensure the power quality. Therefore, AGC's internal algorithms and control links have not changed much compared with the traditional AGC software in EMS. However, the selection and commissioning of AGC in PMOS has undergone fundamental changes compared to traditional EMS. In the electricity market model, the adjustment of AGC as part of the supporting plan must fully consider the new economic factors such as the impact of the unit on the market marginal price of electricity, economic compensation after inputting supplementary services, and so on. At the same time, AGC units must perform AGC reporting. Units that do not have an AGC application must not be put into AGC's auxiliary services.
Although different power market models and operating rules may not be the same for AGC or even other auxiliary services, some domestic and foreign successful approaches are that AGC units will also participate in bidding. It will also have an impact on market marginal electricity prices. This approach can naturally transition to the bidding of the mining auxiliary service market.
It must be pointed out here that, as AGC software of the existing EMS, it can still be used in the power market mode, and it provides interface support with the AGC control system in PMOS.
2.2.2 Load forecasting The traditional concept of load forecasting is to use known historical load data and information on various factors affecting load changes. Various forecasting methods are used to summarize load changes and establish load models.
In the electricity market, the load forecasting model must consider the load response to electricity prices [4]. The electricity price changes with time and the operating state of the grid, and the generating company responds accordingly to the electricity price. When the load is high, the generating company may increase the quotation. The electricity price for a certain period of time will have an effect on the load of this period and the load of other periods. Moreover, the level of load directly affects the unit's access to the Internet and the settlement price, and it has higher requirements for its accuracy. Especially in real-time scheduling systems, ultra-short-term load forecasting is required and the accuracy requirements are also higher. In the traditional EMS, generally only short-term load forecasting is required, the accuracy is between 3% and 5%, and less manual intervention is needed. In the electricity market, the requirements for the load forecasting function will increase, in order to ensure its accuracy. To make full use of the experience of the dispatcher, more manual interventions should be provided in the load forecasting module. The accuracy of ultra-short-term load forecasting should be improved, requiring an average error of less than 1% and a maximum of 3%.
If the existing load forecasting software is to continue to be used in the power market environment, it needs to be improved according to the above requirements, and the prediction result needs to be transmitted to the PMOS through the interface.
2.2.3 Power Generation Plan In the traditional EMS, the power generation plan mainly includes the power supply plan and the unit economic combination, exchange power plan, fuel plan, maintenance plan, reservoir plan and other functions. The operation plan in the electricity market is not only a simple dispatching order, but also needs to coordinate the relationship between market participants and realize the safe and economical operation of the system according to the principle of bidding price [5]. The plan is based on the transaction contract and bid information. It is necessary not only to formulate a power supply plan, but also to formulate an auxiliary service plan, and the process of formulating the plan is interactive. Each time period may also be adjusted as needed, or may be manually intervened.
Compared with the power generation planning module in the traditional EMS, the power generation planning module in PMOS can be summarized as follows:
a. Power generation plan: no longer directly formulated by the dispatcher, but based on the quotations of each generator set, according to the principle of the minimum cost of power purchase according to the order of the highest to the lowest price to formulate [6]: According to different market rules, The power generation plan scheduled one day ahead of time is called a pre-scheduled (spot) plan; the real-time electricity market prepares a real-time generation plan based on the ultra-short-term load forecasting and the real-time reiteration quotation of each power plant unit.
b. Economic Dispatch: Since the production principle of the power generation plan in the traditional EMS is that the system-wide power generation cost is the lowest, after entering the electricity market, for example, in the power market mode where the power generation side is open, a single purchaser represented by the provincial power companies develops the power generation. When planning, on the premise of ensuring system security, it is bound to aim at the lowest cost of electricity purchase. Therefore, the traditional algorithm of economic dispatch (ED) module will no longer meet the needs of the electricity market.
c. Unit economic combination: The unit combination software in the traditional EMS will no longer be suitable for the electricity market model; whether it is the pilot operation of the current power generation-side electricity market in China or the future development of a more open transmission side or entering the retail market. Power generation companies, power sales companies, and power grid operating companies are all independent and self-financing independent interests. The economic benefits of the unit are determined by the power generators themselves, and the power grid operators are responsible for the safety of the power grid.
d. Inter-network power exchange plans; under the electricity market model, economic considerations must also be considered; under the premise that other electricity grids also realize the electricity market, exchange power plans are established based on the principle of lowest cost of electricity purchase and exchange contracts between regions; inter-regional exchange contracts The formulation of the rules should be based on the principle of maximizing profits. In actual market operations, market transactions in this region and other regions can be achieved through agency traders; however, exchange contracts can be negotiated and established when other power grids do not implement electricity markets.
e. Inter-network transaction evaluation: In the electricity market, in order to ensure economical efficiency, it is necessary to compare the actual operation mode with the pre-planned approach and make a short-term evaluation to help the power system personnel determine the power transaction fees with the neighboring power companies. And evaluate whether the transactions made are economically favorable.
L. Cost Analysis of Power Plants; In the electricity market, each power producer is an independent economic entity. They participate in the operation of the power system through online auction of the unit and are fully responsible for their own economic behavior; therefore, the production cost analysis of the power plant It is the behavior of the power generation company, not directly determined by the dispatching and operation department, but the regional and system-wide production costs are still analyzed and formulated by the dispatching and operation department.
g. Hydro-electricity plan and combined thermal and hydroelectric power dispatch: The hydropower project in the traditional power market and the joint economic dispatch of hydro-thermal power must all undergo significant changes in the electricity market. If the hydropower plant participates in market operations as a bidding entity, the hydropower project must obey the system to minimize the cost of power purchases. The needs are arranged by the pre-dispatching system and the real-time dispatching system in the power market. The traditional hydropower project no longer exists; hydropower plants can participate in the market as a fixed output if they do not participate in the market bidding; the joint dispatching of hydrothermal power in the electricity market also No longer exists because the plans for thermal power units and hydropower units are determined by the pre-scheduling and real-time dispatch systems in the electricity market.
Based on the above analysis, it can be seen that in the power market environment, the original power generation planning functional modules of the application software in the EMS will not be able to continue to be used, and the preparation of various plans needs to be completed by the PMOS transaction management system (TMS).
2.3 Network Analysis Level In the traditional EMS software, the function of the network analysis software is to improve the security of operation and make use of the comprehensive information of the power system to make decisions and analysis.
In the power market mode, the main purpose of the power system application software is to eliminate the network insecurity factors based on the constraints of the network and ensure the security of the network and the system based on the price of the power plant bidding unit. The application software in the power market establishes a complete and accurate description of the power system through network modeling and state estimation. The power flow calculation analyzes the trend distribution of the cost-effective online unit in the system. It is envisioned that the fault selection module is used to identify critical faults that may cause unsafe system operation. The safety correction module is used to eliminate the insecurity caused by the output of the bidding grid unit to the network. The optimal power flow module is responsible for the optimal scheduling of all system resources and control methods. The objective function of the above modules should fully reflect the economic principle of the power market and ensure the safety of the power system. If insecurity is found, the electricity market application software will modify the operating plan according to certain rules.
2.3.1 Network Analysis, Modeling, and State Estimation Module The basic algorithm of this module is not much different in the electricity market from traditional EMS. However, the uncertainties of the unit's access to the Internet in the electricity market have increased, and the output of the unit is also subject to major changes. At the same time, factors such as the maintenance plan of the system have to be taken into consideration. Therefore, the importance of these modules in the electricity market is correspondingly enhanced. It will change accordingly. Similarly, the results of these modules will also serve as the basis for other analysis software as network parameters to provide initial data to other modules. The module can continue to be used in the electricity market environment with certain improvements on the original basis.
2.3.2 Power Flow Calculation Module This is a pre-calculated process that calculates the power flow distribution and network loss caused by the spot planning (pre-planning) and real-time planning. In power flow calculations, the active power output of the unit is not the value of telemetry or state estimation, but the planned unit output in the spot planning and real-time planning. Because the power market does not consider the reactive power plan for the time being, the reactive power output of the unit may be taken as a state estimate for a period of time. The load of the node can be obtained through the bus load forecast, or the distribution factor can be calculated by the load distribution of the previous period, and the load forecast value can be distributed to each computing node. Other network parameter values ​​are obtained from state estimation. In the result of the load flow calculation, the congestion of the network should be given.
2.3.3 Dispatcher flow module In the electric power market, the function of the dispatcher's current flow is still the simulation of the dispatch operation or the operating mode. However, the dispatch operation simulation can not only deal with the opening/closing of the switch/switch, but also the transformer. Tap adjustment, unit output and load value increase and decrease, but also to simulate the power plant's quote changes and changes in the schedule caused by the distribution of the trend, as well as the system in the equipment and the whole system of active and reactive power losses. This is not yet available in the existing EMS PAS software functions and needs to be added and improved.
2.3.4 Predictive Accident Analysis (Static Safety Analysis) Module The module can perform automatic fault selection, select a serious accident, and give an alarm of the limit violation. This is the same as the function of the traditional predictive accident analysis module. The difference is that the data source of the predictive accident is the same as the load flow calculation module and is an advanced pre-calculation process. Unit output and nodes are derived from planning software and load software. Moreover, the module is generally started on a time basis, and the pre-planned and real-time planned power generation schedules are analyzed and verified. Of course, this module can also be started by the dispatcher. In the electricity market environment, it can continue to be used after certain improvements.
2.3.5 Safety Correction Module This is an important process in the spot planning (pre-planning) and real-time planning modules. The unit's bidding for the Internet changed the traditional model's power generation plan, resulting in a larger change in the unit's output, and thus a greater change in the system's power flow. As a result, the network's insecurity increased [7]. The security correction module in the power market must be adjusted according to market rules and various technical parameters of the power grid and the unit to ensure the security of the network. In the well-established market rules, clear provisions will be made on the resolution of security issues. The security correction module under market operations shall determine the objective function based on these provisions.
2.3.6 Optimal power flow module The traditional optimal power flow generally takes the minimum cost of power generation and minimum network loss as the objective function, and considers various system constraints and the constraints of the unit's technical parameters. In the market environment, the optimal current must not only consider the technical constraints, but also the constraints of economic parameters such as unit quotes. The objective function with the lowest cost of power generation should also be replaced with the minimum cost for the power grid. The objective function with the smallest network loss can be unchanged, but the impact of network loss on the system is relatively weak, so the preference for the minimum purchase cost is the objective function.
3 Conclusion The introduction of the electricity market has brought about significant changes in the function and content of traditional EMS. This paper proposes the impact of the electricity market on the software functions of existing EMS at all levels, and how to establish a foundation for the establishment of PMOS in the establishment of a new EMS, so as to make full use of existing resources and reduce investment to achieve two systems in the future when establishing PMOS. Smooth transition and seamless integration. Through the above analysis, the following points should be emphasized in the construction of PMOS and the transformation of EMS:
a. According to the definition of “Functional Requirements for the Power Market Technical Support System†issued by the document of the State Power Diversion [2000] 773, the electric energy management system and the electric energy metering system appear as a relatively independent subsystem in the future competitive electric power market. It is part of PMOS.
b. At this stage, they should maintain their relative independence, which can increase the safety and stability of the two systems themselves. Although the two systems are closely linked, their respective purposes and methods are not the same. It is considered that the two systems can be considered together. It is not feasible to extend the functions of the EMS to cover the functions of the PMOS. The practical approach is to keep the two systems relatively independent of hardware setup and software functionality.
c. Improve the openness of the system, can reduce the interface work between modules and systems, improve system efficiency. Although the two systems are relatively opposed to each other in the hardware configuration, there are many common things. As mentioned above, the data source and power system application software, many of the data used by PMOS need to be forwarded from the EMS, so it should be possible to make two The system can be seamlessly connected in many ways.
d. Take full account of the system's scalability. Because of this special relationship between PMOS and EMS in the electricity market, the two systems should be planned and constructed at the same time so that the completed system can achieve maximum efficiency and efficiency, leaving room for the development of the electricity market.
The brine tank is an essential component of water treatment systems, specifically in water softening processes. It is used to store and dissolve the softening salt, allowing it to mix thoroughly and effectively regenerate the resin.
PE (polyethylene) is the material commonly used to manufacture brine tanks due to its desirable properties. PE tanks are resistant to both acid and alkali substances, ensuring that the salt and other chemicals used in the water treatment process do not corrode or damage the tank. Additionally, PE tanks are durable and do not easily deteriorate with age, providing a long service life.
Furthermore, PE brine tanks are non-toxic and tasteless, ensuring that the water being treated remains safe for consumption. This is particularly important as the salt used in the tank will eventually mix with the water supply. The non-toxic nature of PE also means that it does not introduce any harmful substances into the water.
Overall, PE brine tanks play a vital role in water treatment projects by facilitating the proper dissolution of softening salt and enhancing the regeneration of resin. With their various color options, acid and alkali resistance, longevity, and safety features, PE brine tanks are a reliable and efficient choice for water treatment systems.
Brine Tank,Salt Brine Tank,Square Salt Tank,Softener Salt Brine Tank,Softener Salt Tank
Hebei Chengda Water Technology Co.,Ltd. , https://www.arclionchengda.com