Organochlorine pesticides are a broad-spectrum insecticide that has been widely used in the world. Among them, HCH and DDT are used for a long time, with a large amount and a wide range. Although they have been banned for many years, their long-term accumulation in the environment, especially in the soil, due to their lipophilicity, long half-life, and hard-to-degrade properties. The content is high, and then it migrates to plants, vegetables, and Chinese herbs. In recent years, the trend of returning to nature has made people pay more attention to green medicines. The demand for natural medicines in countries all over the world is increasing day by day. Since the last century, pesticide residues of Chinese herbal medicines, especially organochlorine residues, have become China’s Chinese herbal medicines going international. The major obstacles to the market are, therefore, of great importance in standardizing and standardizing the research of organochlorine pesticides in Chinese herbal medicines. China has already established the national standard detection methods and limit standards for HCH and DDT in fruits and vegetables, foods, and oils and fats. There are very few national standard detection methods and limit standards for Chinese herbal pesticide residues. In this study, we determined the determination of eight organochlorine pesticide residues in four Chinese herbal medicines by capillary column gas chromatography for the determination of organic chlorine in rooted Chinese herbal medicines such as ginseng, salvia miltiorrhiza, and licorice bellflower, and provided an effective analytical method for the detection of pesticide residues in Chinese herbal medicine. .
1 Experimental section
1. 1 The main instrument and reagent GC - 6820 Gas chromatograph with ECD detector, DB - 5 quartz capillary column (30. 00m × 0. 32mm × 0. 25m). DDT and HCH standards; DDT and HCH mixed standards (containing 4 DDT isomers and 4 hexan hexaisomers), first dissolved in n-hexane to form a stock solution of 100 μg/L, and reused immediately before use. N-hexane was gradually diluted and formulated as a standard working solution. Acetone, petroleum ether, and n-hexane are chromatographically pure, anhydrous sodium sulfate (burning at 650 °C for 5 h), sodium chloride (baked at 120 °C for 4 h), flororeil silica (baked at 120 °C for 4 h), solids cooled after reagents Both are stored in a desiccator. A soil tester (measures the nutrient content in the soil, such as nitrogen and phosphorus, which is also an aspect of pesticide residues). Soil temperature and humidity recorder.
1. 2 experimental methods
1. 2. 1 Sample Pretreatment Accurately weigh 5g of fully crushed sample in a 250ml Erlenmeyer flask, add 100ml of extractant (40ml of n-hexane + 40ml of petroleum ether + 20ml of acetone), soak for 4h, shake for 1h in a shaker. , Ultrasonic extraction 30min, filtered through a glass sand core funnel, standing stratified. The upper organic phase was transferred and passed through a 10 cm high anhydrous sodium sulfate glass cartridge and washed with a small amount of n-hexane, and evaporated in a water bath at 80° C. to 2 ml, to be purified.
1. 2. 2 Purification of the sample Add 2cm high anhydrous sodium sulfate, 8g of fluorosilicone to the glass column, add 2cm high anhydrous sodium sulfate, and tap. Twenty ml of n-hexane was poured into the column to wet the adsorption column. When n-hexane was near the upper layer of anhydrous Na2SO4, the concentrate was transferred to the column and the concentrated bottle was washed with n-hexane three times. The washing solution was introduced into the layer. Analyze the column and collect the purification solution. When the solution is close to the upper layer of anhydrous sodium sulfate, the column is eluted with n-hexane:acetone (9:1). The column is then incorporated into a concentrator bottle and evaporated to dryness at 80 °C. Dilute to 1 ml for analysis by gas chromatography.
1. 2. 3 Chromatographic inlet temperature 250 ° C, electron capture detector temperature 300 ° C, carrier gas, auxiliary gas are high purity nitrogen, purity 99. 999 %, carrier gas flow rate: 2. 0ml / min, into Sample method: splitless injection, column temperature program: column temperature of 150 °C for 4min, then from 8 °C / min to 220 °C, hold 12min, then from 20 °C / min rose to 270 °C, hold 5min. Injection volume 1μl.
2 results
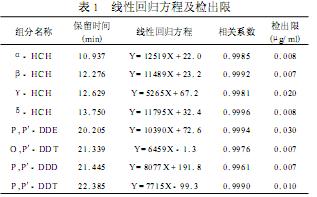
2. 1 linear range and limit of detection with n-hexane 100μg / ml stock solution was diluted to different concentrations of standard solution were subjected to experiments, and to draw a standard curve, the test results show that the measured concentration of the components in 0. 01 The range of ~5. 00μg/ml is linear with the chromatographic peak area. The linear regression equations, correlation coefficients, and detection limits of the eight components of HCH and DDT (S/N = 3) are shown in Table 1.
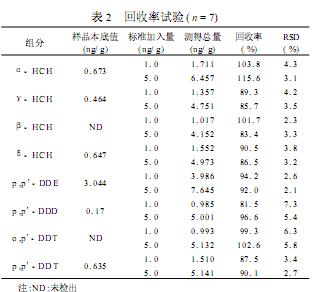
2.2 Method spike recovery and precision Perform intraday and interday precision tests under optimized chromatographic conditions. 3 % of standard solutions of low, medium, and high concentration were tested, and each concentration was tested 6 times in 1d. The intraday precision (RSD) was 3.1%.
5 %~9. 6%之间。 Between ~ 5.4%, the same three kinds of concentrations within the test day 1, continuous test 6d, the precision between days in between 4. 5 % ~ 9.6 %. Take 7 samples of the same Chinese herbal medicine (platycodon grandiflorum) in parallel and add the two concentrations of the mixed standard solution respectively. Since the content of organic chlorine in the Chinese herbal medicine is relatively low, we choose the low and medium concentrations to perform the standard recovery test, and then extract according to the test method. , purification and gas chromatography (n = 7). The results are shown in Table 2.
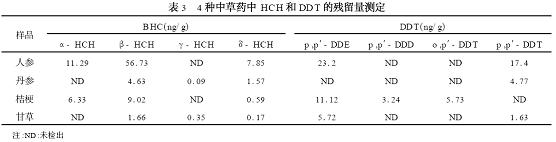
2. 3 Determination of samples Accurately weigh 4 kinds of Chinese herbs, according to "1.2" treatment, external standard method, measured pesticide residues in Table 3, 8 kinds of organic chlorine standards and sample chromatogram shown in Figure 1.

3 Conclusion
This article established a gas chromatographic method for the determination of 8 organochlorine pesticide residues in 4 rooted Chinese herbal medicines. The method is simple and accurate. From the measurement results, eight organochlorine pesticide residues were detected in these four herbs. The content of β-HCH was the highest, and P and P′-DDD were the lowest. According to the limit standard for HCHs and DDTs in the licorice root of the 2000 edition of the 2000 Pharmacopoeia, the organochlorine residues of the 4 Chinese herbal medicine samples tested were not excessive.