[ Instrument R & D of Instrumentation Network ] Recently, the international astrophysics journal The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series published online a research result of the collaboration between Dr. Yuan Zunli, researcher Wang Jiancheng of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Yunnan Observatory, and researcher Wang Jiancheng, and professor Oxford University Matt Jarvis. This research is based on the principle of nuclear density estimation in modern statistics and proposes a universal method for accurately estimating the photometric function. It is of great value for the statistical study of the evolutionary properties of extragalactic objects such as galaxies, active galaxy nuclei, and gamma storms. .
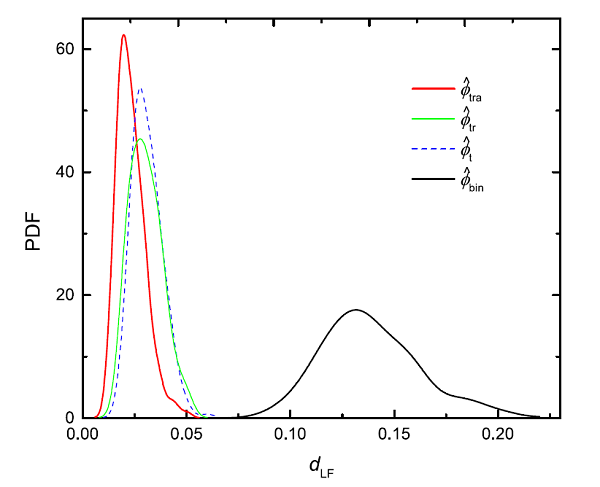
The photometric function is a very basic statistic that reflects the change in the number density of certain types of celestial bodies in the universe with redshift and luminosity (or magnitude). Accurately determining the luminosity functions of various celestial bodies and their evolution has always been an important topic in astronomy. The methods for estimating the photometric function are mainly divided into parametric methods and non-parametric methods. The parameter method needs to assume the form of the photometric function, and obtain the parameters of the photometric function by fitting the observation data, but the disadvantage is that the model is dependent. The non-parametric method starts directly from the observation data and is often estimated using the binning method, but the disadvantage is that the stability and accuracy are low. The mathematical principle of the binning method is a two-dimensional histogram. In modern statistics, the histogram has been seriously outdated as a density estimation tool. Instead, it is kernel density estimation.
Yuan Zunli et al. Proposed a new method for estimating the photometric function based on the latest achievements in the field of statistical research on kernel density estimation, by overcoming some difficulties such as the boundary deviation caused by the sample selection effect. The new method has many advantages, including: no need to assume the form of the photometric function, which can maximize the use of data information; the estimation result is a continuous and smooth function, which can accurately reflect the important characteristics of the photometric function (such as peaks and inflection points); The Bayesian method can reliably estimate the calculation error of the photometric function; it has high flexibility and can be extended to estimate the multivariable photometric function. In short, the new method combines the advantages of parametric and non-parametric methods.
Using Monte Carlo simulation, the researchers found that the estimation accuracy of the new method is nearly an order of magnitude higher than the classic binning method, and the stability is also significantly better than the old method. At present, Yuan Zunli and others are beginning to apply the new method to the MIGHTEE survey data led by Matt Jarvis in order to accurately estimate the photometric function of the radio source and reveal the cosmological evolution of radio galaxies.
The research work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Natural Science Foundation of Yunnan Province, and the Key Laboratory of Astronomical Structure and Evolution of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Steel Pipe,Stainless Steel Pipe,Stainless Pipe,Metal Pipe
Changzhou Chengxin Metal Products Co., Ltd , https://www.chengxinsteeltube.com